Have you already tried losing weight through diet and exercise? Are you in need of an extra kick start to help you achieve your personal goals?
An Intragastric balloon could be the right option for you.
Who is the intragastric balloons procedure for?

An Intragastric Balloon is a non-surgical, temporary procedure which is indicated for adults who have not managed to achieve their own personal goals of weight loss or maintenance.
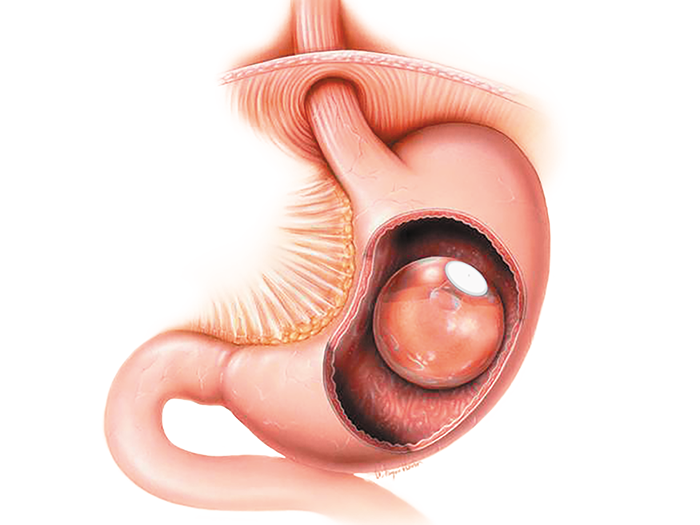
This minimally invasive procedure requires no incisions, stitches, scars, or anatomical modifications. A smooth, soft saline-filled balloon (about the size of a grapefruit) is placed in your stomach.
- Boston Scientific's ORBERA365™ stays in your stomach for up to 12 months.
- Boston Scientific's BIB™ stays in your stomach for up to 6 months.
Pairing an Intragastric balloon with a medically supervised weight management programme could be the solution that you are looking for.
Talk to your doctor about whether you might be a good candidate for this endoscopic procedure.
What is the procedure for placing an intragastric balloon?
The Intragastric Balloon takes up space in your stomach and slows down gastric emptying. This helps to make you feel full sooner and for a longer period of time. This, along with the smaller portion sizes and changes in your lifestyle could result in meaningful weight loss.
The balloon is inserted in a deflated state by an endoscopic (via the mouth) procedure. Once inside the stomach the balloon is immediately filled with saline solution through a small filling tube (catheter). The balloon has a self-sealing valve and once it is filled the catheter is gently removed.
In a US pivotal study of 255 patients, placement procedure time varied between 5 and 45 minutes².
Intragastric balloon system placement
Intragastric balloon system removal
Kick start your weight loss journey: What to expect from an intragastric balloon procedure?
Intragastric balloons help healthier eating habits become second nature. You’ll learn to listen to your body and feel full with less food. So, the weight loss can begin immediately. These habits should continue even after the balloon has been removed to further support with achieving your personal health goals.
Before the procedure
It is important to plan your post-procedure care plan, even before the balloon has been placed. A trained obesity management team will discuss this with you and tailor the programme to suit your personal needs.
First three months
In the first few days after placement, your body should adjust to the balloon. You might feel sick for a few days as you get accustomed to the balloon. Your doctor may prescribe medication to help proactively manage these symptoms.
If you experience severe pain, nausea, or vomiting (particularly if you were already acclimating to the balloon), contact your doctor without delay. There could be a problem with your balloon that needs attention.
The adjustments to your eating habits and your continued efforts to stay active will greatly influence your results.
Months four through six or twelve
The balloon helps train your body to feel full on smaller portions.
The goal of this period is to continue to build strong habits and prepare your mind and body to keep the weight off after the balloon is removed. Continue to work with your care team to optimize your daily nutrition, diet, and exercise routine.
Success after removal
Depending on your care plan, the balloon will be removed at either 6 or 12 months.
This is officially where all the hard work pays off. Now, you’ve retrained your body to know what full really feels like. Plus, you’ve been weaving more nutritional meals into your diet. These lifestyle changes will help you as you continue on your journey.
Proven results with intragastric balloons
More weight loss than diet and exercise alone³.
Devices distributed worldwide in over 80 countries⁴.
Orbera365ᵀᴹ and BIBᵀᴹ System are CE-Marked under the European MDR
Intragastric balloons patient story: Meet Charlotte
“Life after the Orbera365™ 12 month balloon has been absolutely fantastic.”
Meet Charlotte, a patient who opted for the intragastric balloon procedure to accomplish her weight loss goal.
Intragastric balloons FAQs
All procedures have risks. Patients should talk with their doctor and understand all risks before having any procedure.
To qualify for IGB, you must be an adult, have a body mass index (BMI) greater than 30, who have failed to achieve and maintain weight loss with a supervised weight-control program, and be willing to participate in a medically supervised program.
It is important to understand that the balloon is a tool to aid weight loss and must be used in conjunction with diet, exercise, and a behavior modification program. The amount of weight you lose and maintain will depend on how closely you follow your diet and adopt long-term lifestyle changes. IGBs clinical studies have shown that weight loss varies from person to person. On average, patients lost 3.1x the weight of those who were on a diet and exercise program alone2. In the US clinical study patients lost an average of 21.8 lbs.
Intragastric balloons have been reviewed in over 250 published global clinical papers, and a balloon leak or deflation after placement is reported to occur in less than 1 in 100 patients over 12 months. However, if the balloon should spontaneously deflate, you may no longer feel full after eating. If you suspect this may be the case, notify your doctor immediately. A simple abdominal X-ray can determine if the balloon has deflated. If it has, your doctor will arrange to remove the deflated balloon.
Published clinical studies3 have shown that, provided patients keep to the prescribed diet and exercise regime, patients maintained weight loss through dieting after removal. So, if you stick to your new, healthy lifestyle, you will be well on the way to maintaining your weight loss.
It is very likely the presence of the balloon in the stomach will cause nausea or vomiting after placement. In some patients, it may last one to two weeks. Your doctor may prescribe medication to help minimize these potential effects. Patients will need to immediately contact their doctor for any severe or unusual symptoms, such as severe pain or vomiting.
The balloon can also get bigger while it’s in your stomach. This is reported to occur in approximately 1 in 300 patients. If you think the balloon is getting larger, contact your doctor. An X-ray can be performed to confirm whether this has happened. If it has, the balloon should be removed.
The balloon is constructed of a very smooth and soft silicone material to minimalize the risk of irritating the stomach wall. You will also be prescribed medicines that will reduce the acidity in your stomach and help protect your stomach wall. Patients with prior stomach surgery are not eligible for the procedure because of a higher risk of the balloon causing perforation in the stomach. Some patients without prior stomach surgery have also had stomach perforations. Patients should be advised to immediately contact their physician if they are experiencing severe pain and nausea. The balloon may need to be removed.
The balloon should be removed at the stated time. Leaving the balloon in your stomach for a longer period increases certain risks, most notably deflation of the balloon. If the balloon does deflate, there is a risk of it causing an obstruction in your stomach or intestines. This happens rarely, but you should schedule your balloon removal soon after your balloon is placed, so that there is no delay.
